Causal Inference
Estimating causal effects from observational and interventional data
My research investigates the causal effects of social media interventions on the spread of online harms.
- Identifying the Causal Effects of Twitter’s interventions on Trump’s tweets slides
- Identifying the Causal Effect of the Reduction of Feedback on the Sharing of Low-Quality News Online
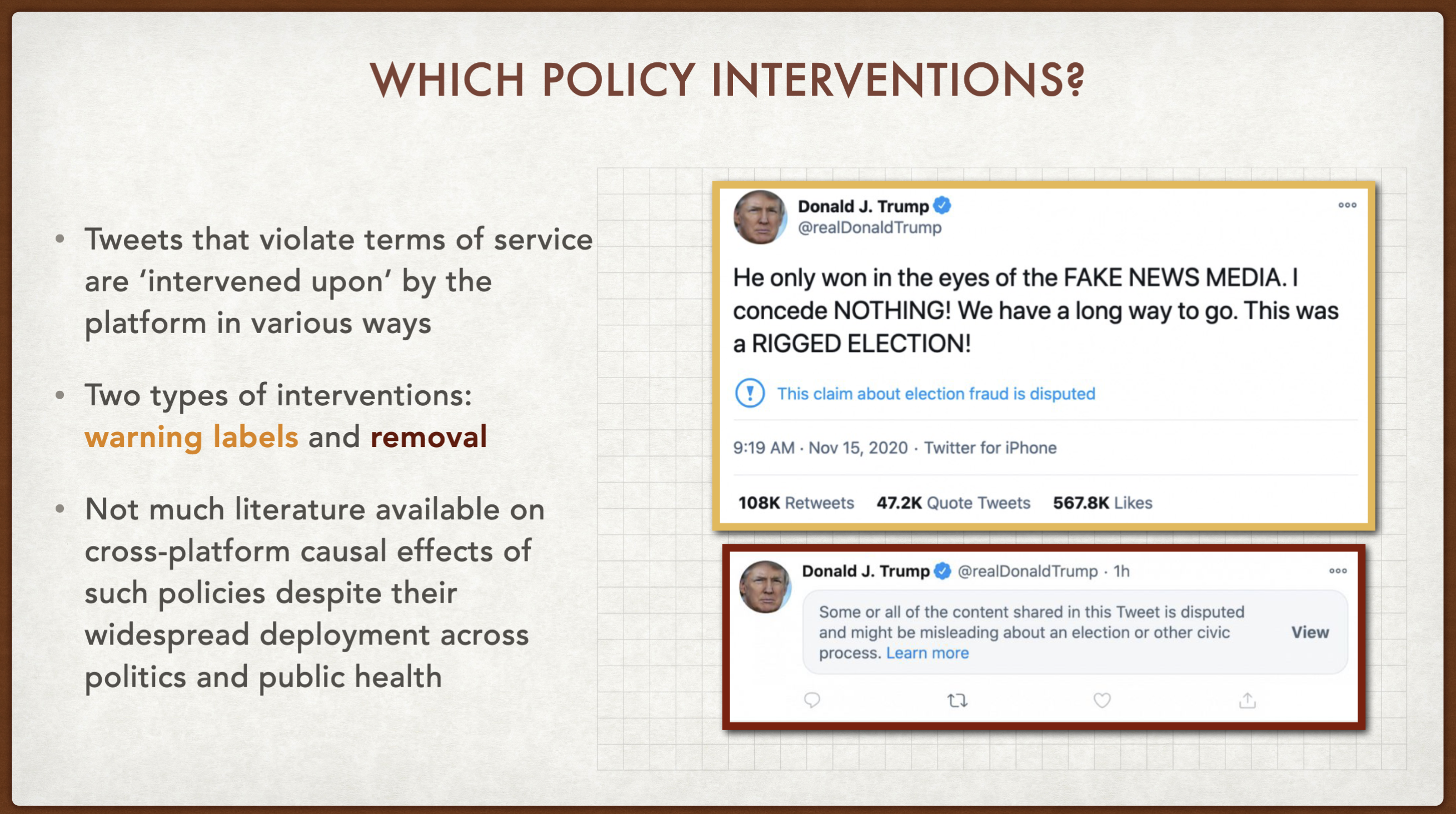
Causal Effects of Interventions
I am interested in examining the impact of interventions taken by social networks to limit the spread of misleading claims online. In recent work at NYU Center for Social Media and Politics, I extend the analysis of Sanderson et. al, 2021 to estimate the causal effects of warning labels and tweet removal that Twitter performed on Donald Trump. Going beyond what platforms are able to do, as external researchers, we studied the effects that Twitter’s interventions had on the sharing of the labeled tweets outside of Twitter, i.e. on Facebook, Instagram, and Reddit. The results were presented at the Stanford Internet Observatory’s first Trust and Safety Research Conference, 2022.
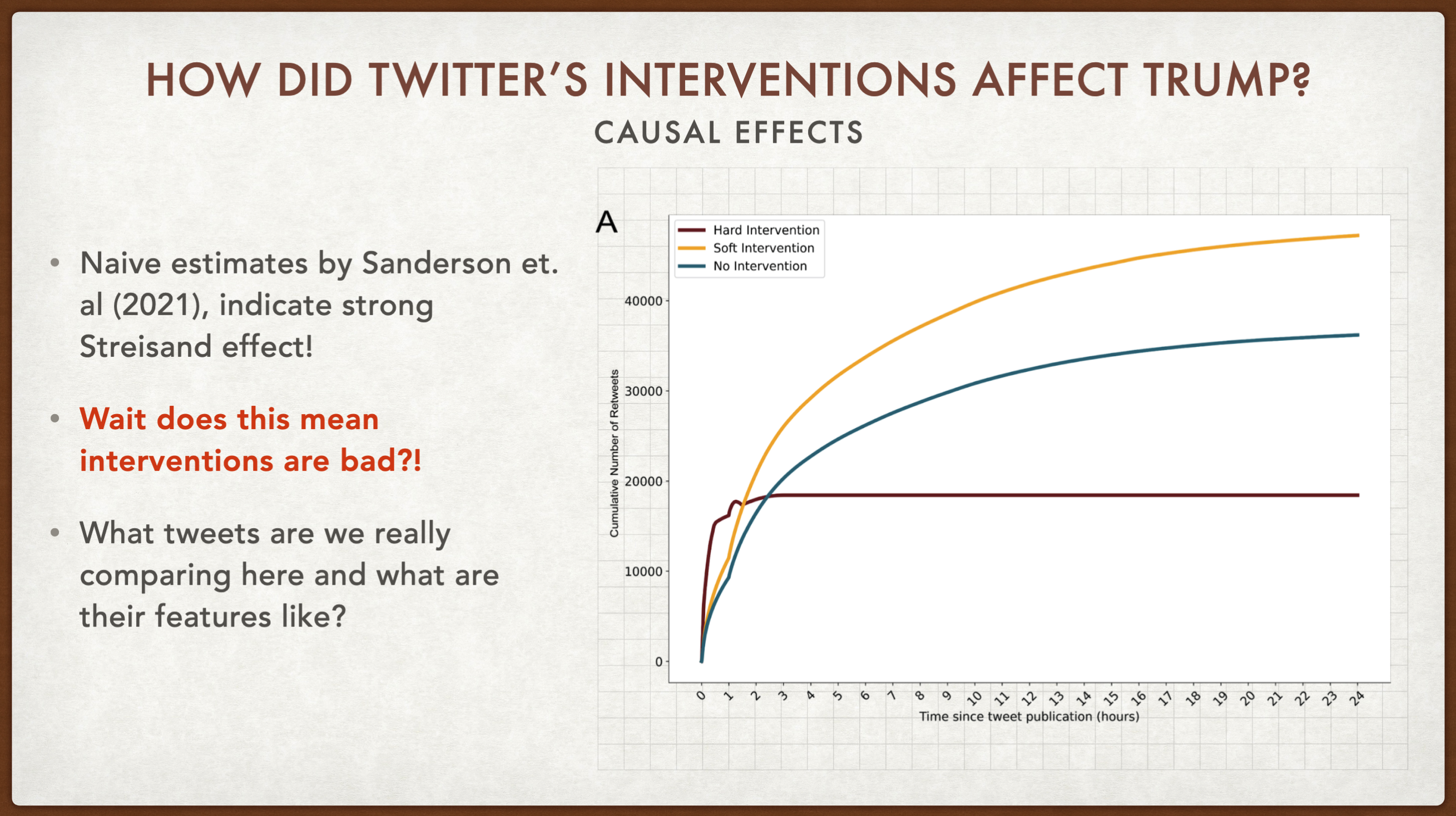
Causal effects are typically challenging to estimate in a network context and almost always limited to individual platforms, so I’m excited to be able to move the needle on approaches to identify novel interventions and use synthetic counterfactuals to estimate the average treatment effect in temporal settings.